Leveraging and Integrating Standardized Language for Predictive Toxicology
- Carolyn Mattingly, Associate Professor, NC State University
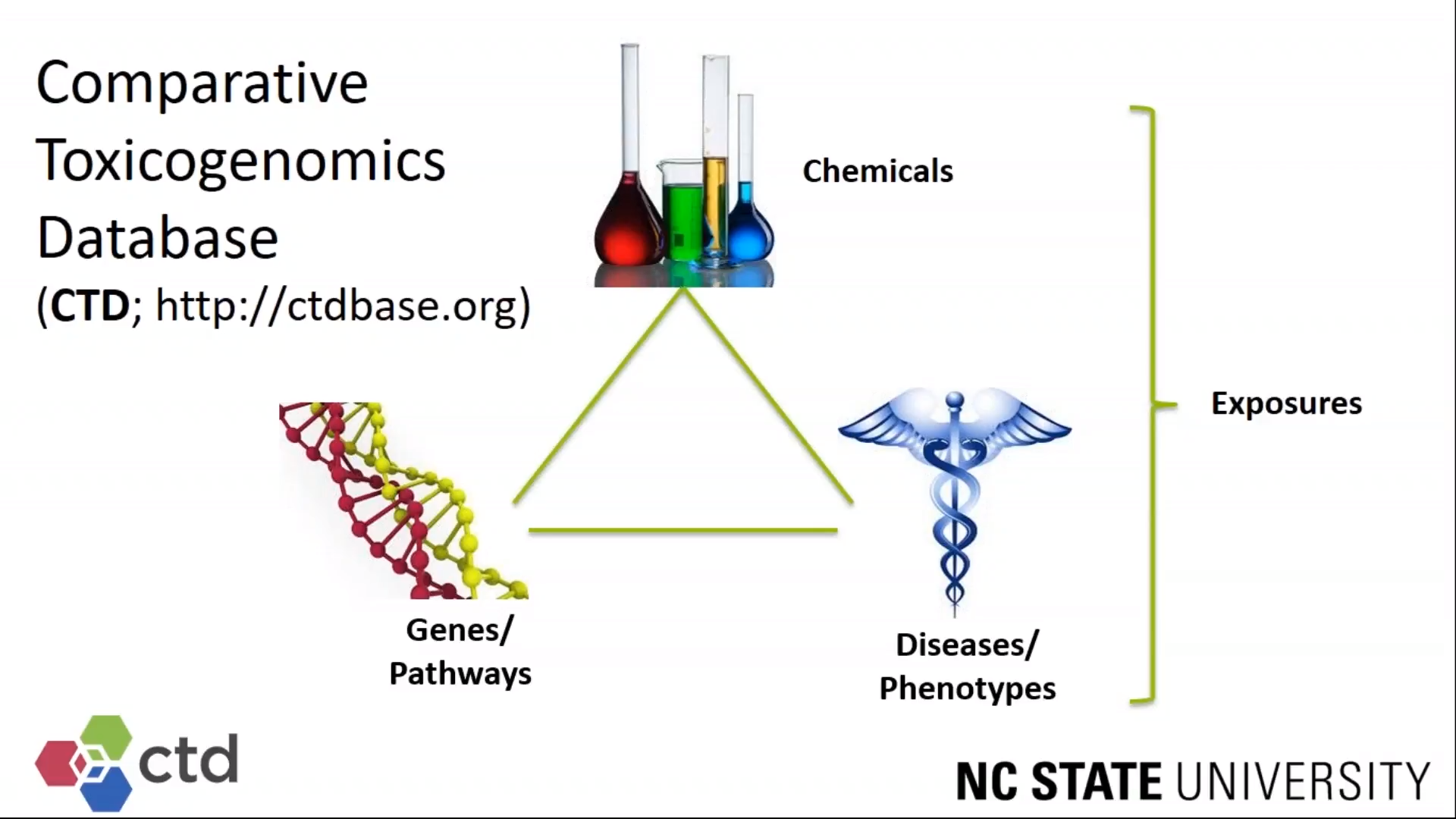
The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD; http://ctdbase.org) is a publicly available scientific resource that aims to inform understanding about the molecular mechanisms by which environmental exposures affect human health. CTD’s content is literature-based and derived by manually curating data modules, including toxicogenomic (for chemical-gene interactions), disease (for chemical-disease and gene-disease associations), phenotypes, and exposure (relating environmental stressors, populations, events, and outcomes) cores. All data points and relationships are captured using standardized vocabularies and ontologies, some of which we developed or modified (e.g., ExO and MEDIC, respectively), in order to integrate across data types and facilitate identification of connections that are otherwise difficult to discern in the published literature.